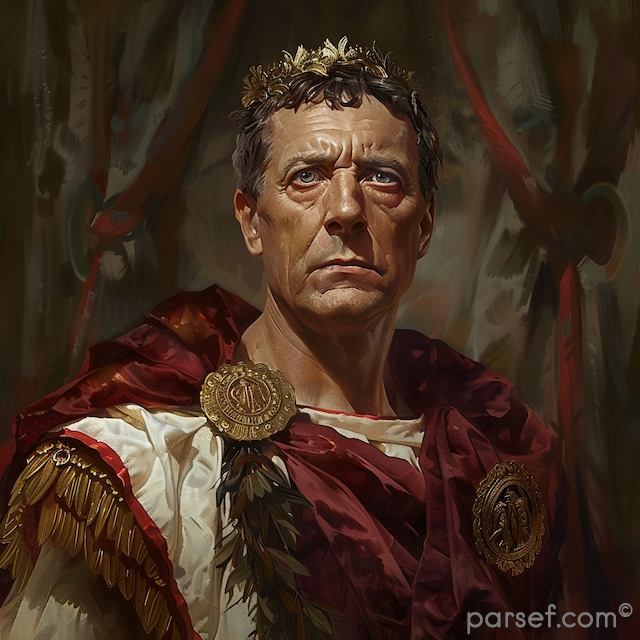
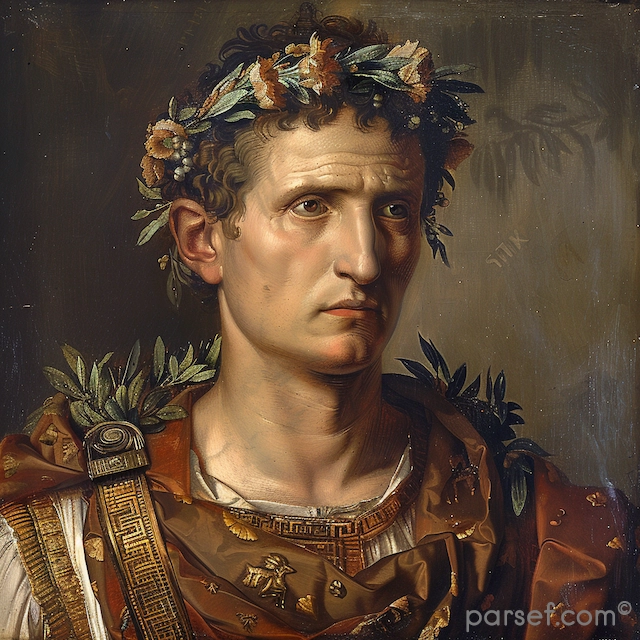
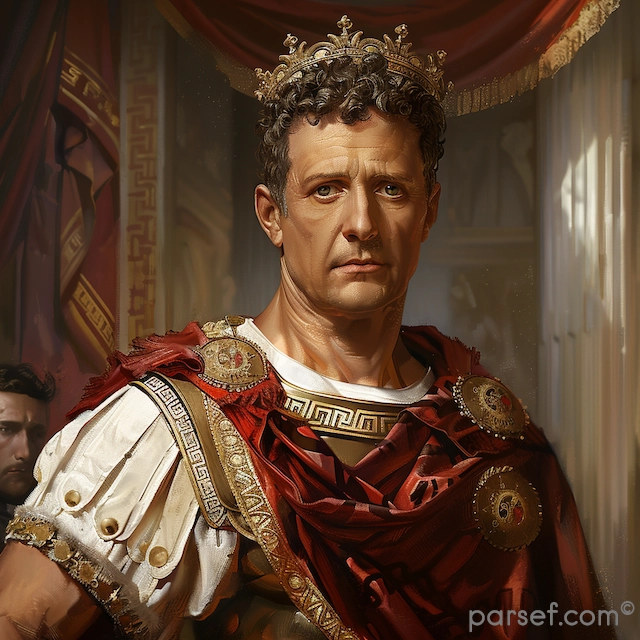
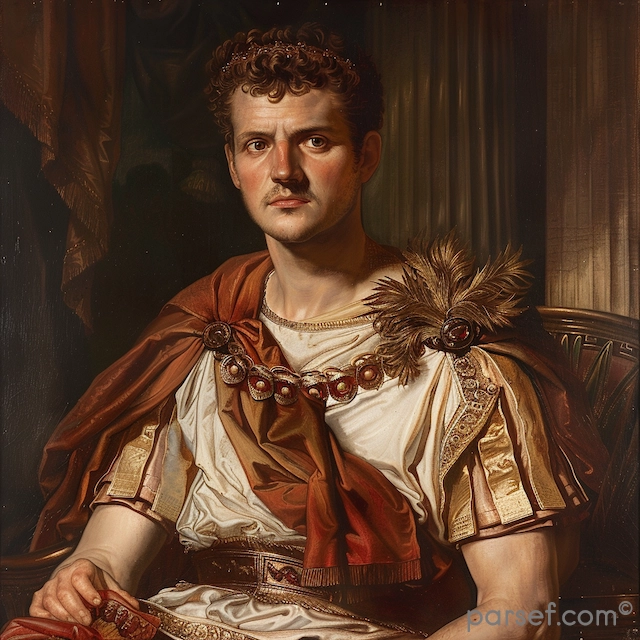
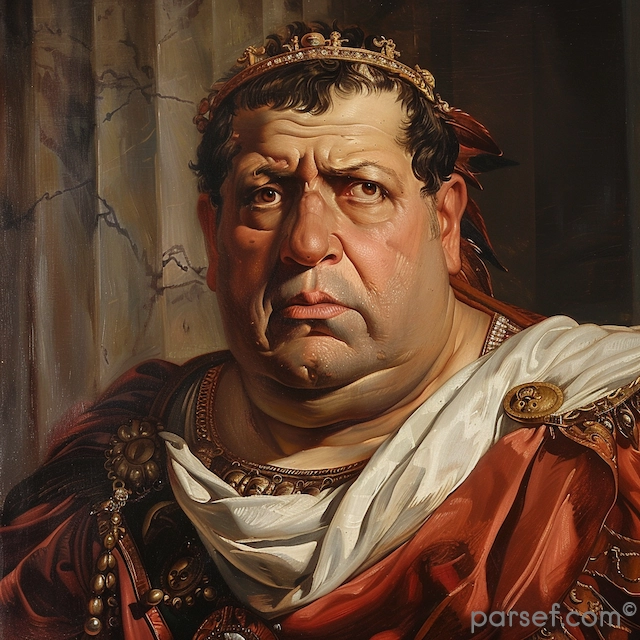
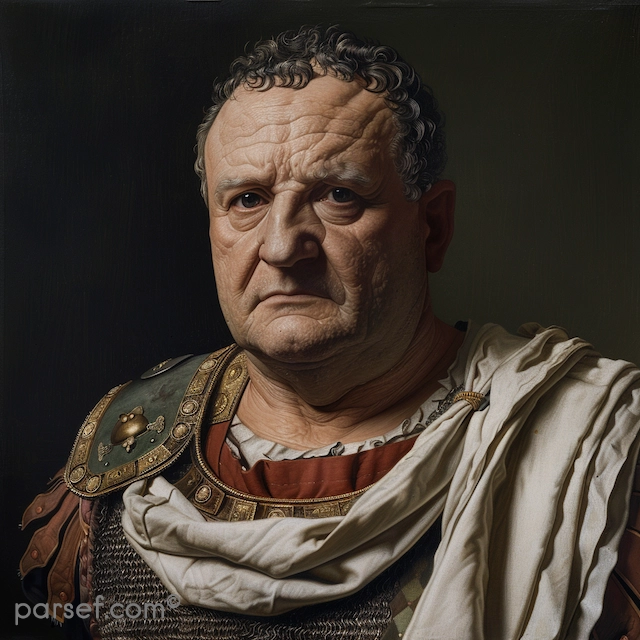
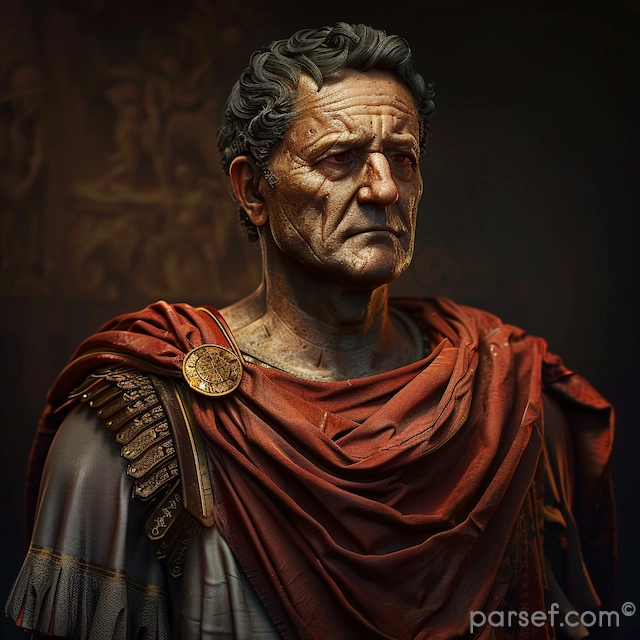
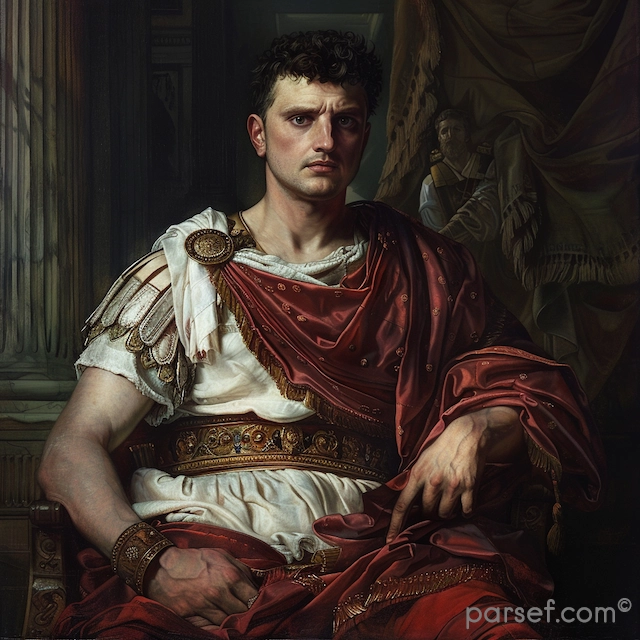
Domitian: The Last of the Flavian Emperors and His Reign of Terror
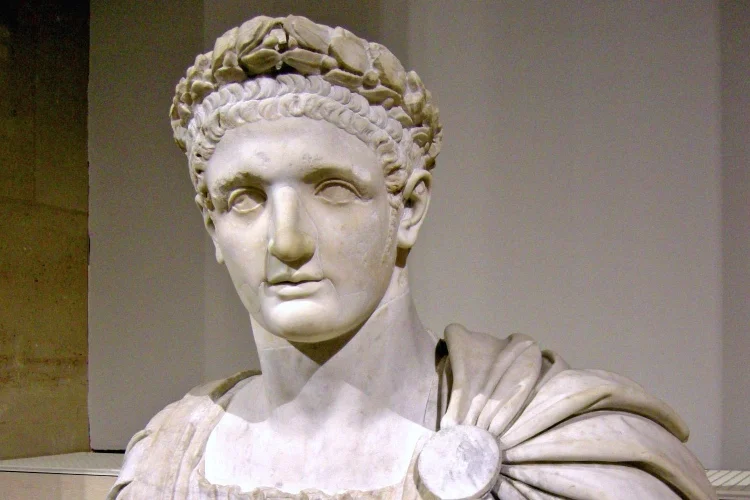

In the annals of Roman history, the reign of Domitian, the youngest son of Vespasian and the last of the Flavian emperors, is often remembered as a time of tyranny, repression, and political intrigue. Domitian's rule, which lasted from 81 to 96 CE, stands in stark contrast to the relative stability and prosperity of his predecessors. In this article, we delve into the life and controversial reign of Domitian, exploring the aspects that earned him a reputation for autocracy and fear.
Early Life and Rise to Power
Domitian was born in 51 CE, and from a young age, he was groomed for a future role in Roman politics. He held various offices, including military commands, before ascending to the throne in the aftermath of his brother Titus' death. Domitian's accession marked the final chapter of the Flavian Dynasty, and his rule was marked by a desire to assert his authority and consolidate power.
Authoritarian Rule and Personal Cult
Domitian's reign is characterized by a pronounced authoritarian streak. He sought to centralize power in the emperor's hands and diminish the influence of the Senate. To this end, he revived many of the imperial court's ceremonial and ritualistic elements, promoting a personality cult around himself.
One of his more controversial actions was the establishment of the "Master of the Horse," a position designed to act as his personal enforcer. This move, coupled with the purges of perceived enemies and critics, created an atmosphere of fear and suspicion in Rome.
Repressive Policies and Persecutions
Domitian's rule saw a series of repressive policies and persecutions. He took a hardline stance against perceived threats to his rule, conducting trials for treason and executing or exiling those deemed disloyal. Intellectuals and philosophers who were critical of his regime faced persecution.
One of the most notorious aspects of Domitian's reign was his persecution of Christians, which marked one of the earliest systematic attempts to suppress the emerging Christian community in the Roman Empire.
Building Projects and Achievements
Despite his authoritarian rule, Domitian did undertake some notable building projects. He completed the construction of the Roman Forum and initiated the construction of the Arch of Titus, a monument commemorating the Flavian victory in Judea.
Assassination and Legacy
Domitian's reign came to a violent end when he was assassinated in 96 CE. The conspirators included members of his own court, highlighting the extent of discontent with his rule.
Domitian's legacy is a complex one. While he left behind notable architectural achievements, his reign is marred by a reputation for autocracy and cruelty. His lasting impact on Roman history is a reminder of the potential dangers of unchecked imperial power and the consequences of suppressing dissent and opposition.
Domitian, the last of the Flavian emperors, remains a polarizing figure in Roman history. His reign, marked by authoritarianism and persecution, is a testament to the complexities of imperial rule and the enduring debates surrounding the balance between centralized power and individual liberty in the ancient world.
Related Posts
Macrinus: The First Equestrian Emperor and His Brief Attempt to Stabilize Rome
Opilius Macrinus, an unexpected figure in the annals of Roman history, ascended to the imperial throne in 217 AD after the assassination of Caracalla. Unlike his predecessors, who hailed from the senatorial aristocracy, Macrinus was an eques, a member of the equestrian order, a social class traditionally associated with business...
Read MoreUnearthing History: Julius Caesar’s Artifacts and Their Significance
Julius Caesar, one of the most renowned figures of Roman history, left an indelible mark on the ancient world. His military conquests, political reforms, and dramatic death have made him a central figure in historical and archaeological studies. Although Caesar lived over two millennia ago, numerous artifacts associated with his...
Read MoreCaracalla: The Emperor of Bloodshed and the Architect of Roman Citizenship
Caracalla, son of the formidable Emperor Septimius Severus, is a complex and contradictory figure in Roman history. Often remembered for his brutality and paranoia, he is equally renowned for one of the most far-reaching edicts in Roman law. His reign was marked by a tumultuous blend of violence and reform. Shortly...
Read MoreCommodus: The Emperor Who Blurred the Lines Between Rome’s Greatest Ruler and Its Most Notorious Madman
Commodus: a name that evokes both awe and abhorrence. Son of the legendary Marcus Aurelius, philosopher-emperor and author of the iconic Meditations, Commodus inherited a realm at the zenith of its power. Yet, his reign would irrevocably alter Rome's trajectory. Was he a brilliant general, a cunning politician, or a megalomaniacal...
Read MoreThe Role of Horses in the Roman Empire: From War to Sport
If we look back on the Roman Empire, we can see that horses played an important role. They were engines of power and symbols of prestige, and they were used for agriculture, traveling, warfare, and yes, entertainment like chariot races. Spanning centuries of conquest and culture, horses have always been closely...
Read MoreA Journey Through Time: Mapping Ancient Rome and Jerusalem
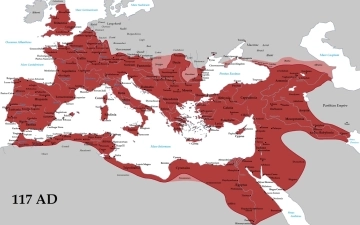
For centuries, Rome and Jerusalem have captivated historians and travelers alike. These two powerful cities, though geographically distant, were intertwined throughout much of their ancient history. But how close were they? Let's explore maps depicting these ancient cities and their respective empires. The Mediterranean World: A Roman Sea During the height of...
Read More