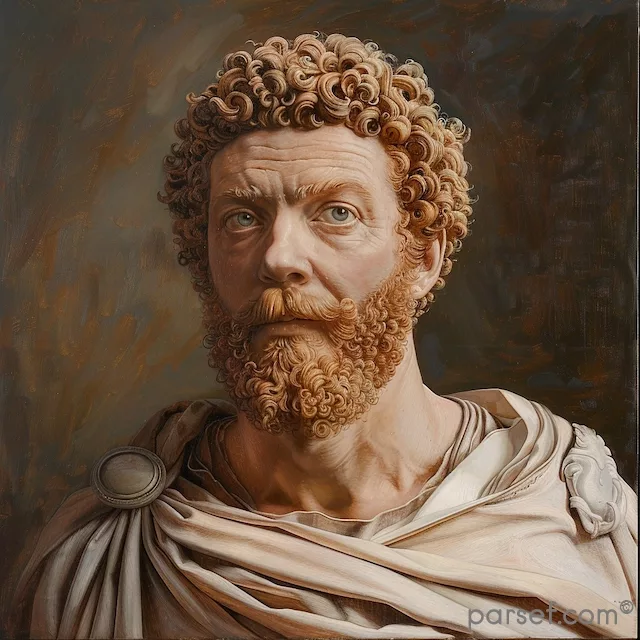
Marcus Aurelius: Philosophy and Leadership in the Midst of Turmoil
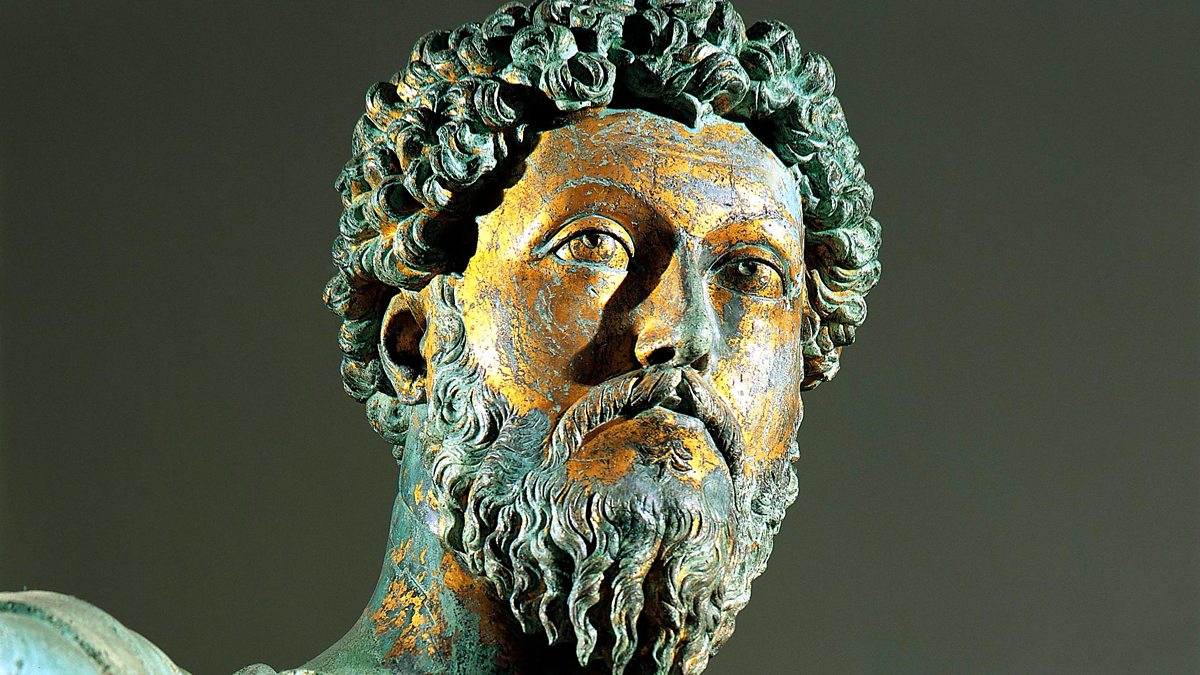

In the annals of Roman history, the name Marcus Aurelius stands as a symbol of wisdom, Stoic philosophy, and leadership during times of great adversity. His reign as Emperor from 161 to 180 CE coincided with challenging periods for the Roman Empire, including external threats and internal strife. In this article, we delve into the life and reign of Marcus Aurelius, exploring how his philosophical beliefs shaped his leadership during tumultuous times.
Early Life and Education
Marcus Aurelius Antoninus was born in 121 CE into a prominent Roman family. From a young age, he received a comprehensive education in literature, philosophy, and rhetoric. His early studies in Stoicism, a school of philosophy that emphasizes virtue, self-control, and rationality, would profoundly influence his life and reign.
The Five Good Emperors
Marcus Aurelius is often counted among the "Five Good Emperors," a period of relative stability and prosperity in the Roman Empire. His accession to the throne in 161 CE was marked by a shared rule with Lucius Verus. However, his co-emperor's early death placed the full burden of leadership on Marcus Aurelius' shoulders.
Stoicism and Leadership
Marcus Aurelius' reign was marked by his commitment to Stoic philosophy, which provided him with a moral and ethical framework for leadership. He believed in the importance of duty and virtue, emphasizing the well-being of his subjects above personal gain.
During his rule, the Roman Empire faced numerous challenges, including the Parthian War, the Antonine Plague, and invasions by Germanic tribes. Marcus Aurelius maintained a Stoic composure, often recording his thoughts in a series of personal writings known as the "Meditations." These writings provide insights into his philosophical outlook and his commitment to rational decision-making in the face of adversity.
Philosophy and Personal Ethics
In the "Meditations," Marcus Aurelius reflects on Stoic principles such as self-discipline, resilience, and the importance of distinguishing between what can be controlled and what cannot. He emphasizes the impermanence of life and the value of living in accordance with reason and virtue.
Legacy and Influence
Marcus Aurelius died in 180 CE, leaving behind a legacy as one of Rome's most respected emperors. His Stoic philosophy and ethical leadership continue to inspire leaders, philosophers, and individuals seeking guidance in facing life's challenges.
His writings in the "Meditations" have been translated and studied for centuries, offering timeless wisdom on topics ranging from personal ethics to leadership principles. Today, Marcus Aurelius is celebrated not only as a wise emperor but also as a philosopher-king whose enduring influence extends far beyond the boundaries of the Roman Empire.
Marcus Aurelius' reign serves as a testament to the power of philosophy in guiding leadership and personal conduct. His steadfast commitment to Stoic principles in the midst of turmoil showcases the enduring relevance of ancient wisdom in navigating the complexities of life and leadership.
Related Posts
Boost Productivity Respectfully: Non-Intrusive Alternatives to Screen Capture Monitoring
Screen monitoring has become essential in modern work environments, particularly with the shift towards remote and hybrid models. Many companies utilize screen capture tools to ensure productivity. But is this the best way to enhance employee performance? Overview of screenshot-based monitoring Screen capture employee monitoring is a popular tool used by managers...
Read MoreClaudius: The Unexpected Emperor and His Surprising Achievements
In the annals of Roman history, the name Claudius stands out as a remarkable story of an unexpected emperor who defied the odds and left behind a legacy of significant achievements. Often underestimated due to physical disabilities, Claudius rose to power and proved to be a capable and innovative ruler....
Read MoreFrom Ancient Rome To Today: 4 Games Played By Emperors And Their Modern Equivalents
In history, Ancient Rome had rulers who enjoyed games that involved intelligence and risk-taking. The interesting part is that some of these games have now evolved to their modern versions that still entertain people. When we look at the Ancient Roman history of emperors having fun, most of them went for...
Read MoreRoman Emperors and the Importance of the Catholic Jubilee of 2025
Throughout history, Roman emperors have played a crucial role in shaping the world, particularly in their influence over politics, religion, and culture. Their legacy continues to resonate today, especially in the traditions of the Catholic Church. One such tradition is the Catholic Jubilee, a sacred year of forgiveness, renewal, and...
Read MoreUnearthing History: Julius Caesar’s Artifacts and Their Significance
Julius Caesar, one of the most renowned figures of Roman history, left an indelible mark on the ancient world. His military conquests, political reforms, and dramatic death have made him a central figure in historical and archaeological studies. Although Caesar lived over two millennia ago, numerous artifacts associated with his...
Read MoreBonsai Trees: The Art, Care, and Beauty of Miniature Trees
Bonsai trees are more than just plants—they are living works of art, shaped and nurtured over time to reflect nature’s beauty in miniature form. Originating from ancient Asian traditions, bonsai trees symbolize harmony, patience, and balance, making them a meaningful and meditative hobby for plant lovers worldwide. Whether you're a...
Read More