Majestic Ancient Rome: Unveiling the Timeless Splendor of Ancient Roman History Architectural Marvel and Colosseum

Introduction
The history of Rome is an intricate weave of power, culture, and art. It gives ample narratives ever since the rise of the Roman Republic until the Empire Era Greco-Roman civilization is captivating for the world, historians and travelers as well. In this article we tell the story of roams where ancient Rome secrets are bound to be fulfilling. From the glimpse of Colosseum as well as the modern diving into the heart of bangercasino.org entertainment. Rome is embellished beauty. It is a life. In this narrative, simultaneous accounts of the past, documents, and structured charts, sophisticated graphics of timeless memories, and important intervals of time are presented along with astounding captions of the milestones of Western civilization.
Ancient Roman History: Foundations and Myths
Etymology and Legendary Origins
It is extremely hard to believe that the first chronicles of Rome encompass myths and marvelous stories. The legend articulates Romulus and Remus in a way where it indicates the two siblings, twins, that were raised by a she wolf constructed the city in 753 BC. It was the starting point of the story that turned into Romans evolution as a civilization and cultural superpower.
Right off the bat, Rome before all else struggled as a city in an attempt to survive because it constantly had to fight for land which would help create a community that could mark its identity for years to come.
Early Social and Government Structures
In the beginning, Rome transformed from a small Village to a developed Society which integrated a blend of Monarchy, Republican and eventually Imperial rule. For Romans to be the dominant force in the Mediterranean Region, there was a need to put in place frameworks regarding the social and political structure as well as judicial and military institutions.
Table: The Early Milestones and Legend Events Between 753 – 264 of the Roman Era
Date/Segments |
Epic Milestone/Legends |
AC Events/Legend Milestones / Legendary Order |
753 BC |
Romulus and Remus founding. |
Forming myth and identity for Rome. |
509 BC |
Republic proclaimed initiated. |
Adoption of principles split the bask of Rome’s smooth democracy. |
396 BC |
Decline, dispossession by the Gauls, primary rapid. |
Need for military change, bound urban reconstruction. |
264–146 BC |
Roman Great Wars. |
Competing acquired Roman global influence, passing through the Shenean Sea. |
The Republic: A Period Characterized by the New Frontiers and Innovation
Defining Features: Marked by Shrewd Politics Alongside Great Public Responsibility
The Roman Republic emerged as an era of civic virtue and prurient political innovation. With systematic checks and balances the Senate, Consuls, and Popular Assemblies jointly steered the state through both tempests and triumphs. Rome’s governance model served as a blueprint for republican democracies to come and shaped political discourse for centuries.
Military Prowess: Conquering Territory
Rome's voracious expansion was underpinned by her military might: a disciplined legion bursting with unrivalled and unyielding spirit of soldiers. Tactical innovations stemmed from the republican control over colossal territories. These conquests not only expanded Rome's borders, but also brought together myriad cultures under the melting pot of Rome.
Milestone table in republican military expansion issue/development timelines histories impact
- Latin War 340 - 338 BC Increased roman hegemony over latino tribes.
- Punic Wars 264 - 146 BC Carthage defeated absolute economic control of the Mediterranean Sea.
- Macedonian Wars 214 - 148 BC Commenced use of Greece and Eastern Mediterranean as emerging superpower.
- Gallic Invasions 390 BC (Sack of Rome) Encouraged building military infrastructure and reformist policies for the arms of Rome.
The Golden Age: Imperial Rome and a Showcase of Architectural Timeless Splendor with Colosseum
Rise of the Empire
Transitioning from a Republic to an Empire was one of the most pivotal moments in the history of Rome. The ascension of Augustus and the Era of Pax Romana brought with it unprecedented periods of peace, stability, and economic flourishing. Marks of this golden period also include the construction of colossal buildings, exceptional infrastructure, as well as widespread arts and literature.
Architectural Wonders and City Structuring
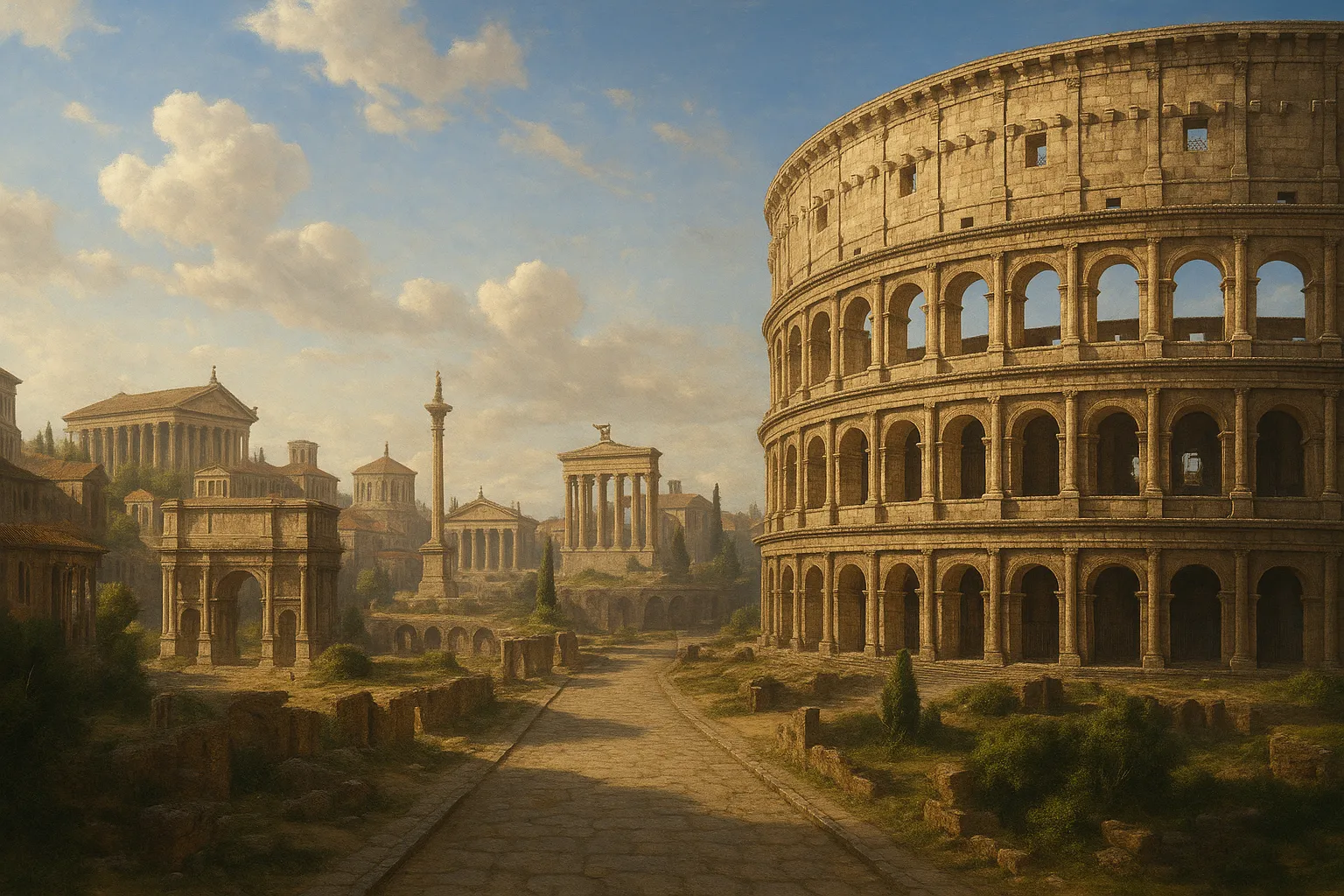
As the title suggests, the Rome Empire was characterized by massive building works. Construction of the extraordinary Colosseum, the staggering Pantheon and a myriad of roads and aqueducts, not to mention Rome's prestige and technologies. These buildings served and continue to accomplish functions alongside Rome’s legacy.
Table: Iconic Architectural Achievements of Imperial Rome
Structure/Project |
Construction Period |
Key Features and Significance |
Colosseum |
AD 70-80 |
Amphitheater for public spectacles and gladiatorial contests. |
Pantheon |
AD 118-125 |
Architectural marvel with a revolutionary dome design. |
Roman Roads |
Various (Republic to Empire) |
Network of roads facilitating trade, military movement and communications. |
Aqueducts |
312 BC - AD 226 |
Advanced engineering feats delivering water to urban centers. |
Cultural Flourishing and Intellectual Legacy
The golden age of Rome was also a period of cultural and intellectual prosperity. Literature, philosophy and arts were exceptionally supported by the emperors and aristocratic class. Works of poets like Virgil, Horace and Ovid marked the rich literary tradition with some of the most remarkable poetry and profound commentaries on humanity. This cultural renaissance is regarded as the cornerstone of the Western civilization and it certainly inspires contemporary art and literature.
Life on a Day to day Basis in Ancient Rome
All Neighborhoods within the community along with their Social Life
Every early Roman was rich, but simultaneously faced constant difficulties. The economic pyramid consisting of rich patricians on top and poor plebeians at the bottom, was present in Rome as well. Religion was also a major factor in the day-to-day life of ancient Rome, and the constructions of the forums, piazzas, markets, and public baths helped increase the social interactions between citizens.
Table: Social Structure in Ancient Rome
Social Class |
Explanation |
Functions in Community |
Patrician |
Politically prominent aristocratic families |
Managed the state and occupied key posts in ruling. |
Plebeians |
Common people engage in a variety of professions. |
Served as the backbone of the Roman economy. |
Freedman |
Former slaves who were granted freedom and higher status in society. |
Helped to develop business and commerce. |
Slaves |
People legally bound to work as servants and laborers. |
Did the most basic work in homes and construction sites. |
Innovative Civil Building Projects
Rome was a major political and cultural center with unrivaled urban and civic planning. The establishment of public baths, amphitheaters, and comprehensive healthcare left for centuries bathing hygiene and public hygiene in Rome. Improvement in life standards for Roman citizens set the coming history.
Leisure, Dining, and Hobbies
From grand feasts to attending the theaters, with an added bonus of watching gladiatorial and animal combats, there was no shortage of activities for the people to do in ancient Rome. Due to the empire’s extensive reach, Ancient Rome was known for its delectable cuisine. Activities offered to the public such as horse racing, chariot racing, and dramatic performances were also very entertaining.
The Enduring Aspirations of Rome
The Evolution
Even with the fall of Western Roman Empire, its impact was felt throughout the world for years on end. The legal, cultural, and architectural impacts of Rome are still remembered in today’s society. An example of this is how many countries base their legal frameworks off Roman laws. Modern architects and city planners also took note of the brilliant construction and design methods used by Roman engineers.
Preservation of History and Discovered Relics
It is imperative that the history of ancient Rome is kept alive through archaeological excavations and documenting ancient Roman civilization. Numerous ruins, pieces of art, and various items discovered within the city portray life from a bygone era. Given enough time in Rome, museums, the Roman Forum, and Palatine Hill will be met which exhibit not only immense portions of Rome's history, but allow one to feel and understand what life in ancient civilization was.
Table: Major Archaeological Sites in Rome
Site |
Description |
Historical Significance |
Roman Forum |
Center of ancient Rome’s political and social life |
Heart of public life and governance |
Palatine Hill |
Legendary birthplace of Rome and site of imperial palaces |
Symbolizes the origin and power of Rome |
Colosseum |
Iconic amphitheater used for public spectacles |
Represents Roman engineering and social culture |
Catacombs |
Underground burial sites reflecting early Christian communities |
Provide insights into religious practices and societal transitions |
Rome in Modern Imagination
Influence on Art, Literature, and Popular Culture
Historically significant places across the globe can have a lasting impression over modern art and literature, take for example Rome. Movies, books, and artworks capture the essence of ancient Roman stories and augment its narratives. Such timeless Rome fascination emphasizes its distinguishing mark as the best city in the world which history remembers and people still cherish.
Intellectual Impact and Academic Activities
Rome is at the center of study and contemplation for educated people and scholars due to its profound influence on modern civilization, politics, culture, and society as a whole. There are learning institutions specializing in classical studies that teach the philosophy, arts, and political life of ancient Rome. These activities go a long way in preserving the past and enriching contemporary debates on politics, metropolitan planning, and national identity.
Tourism: Reaching the Aspirations of the World
Rome is currently an open-air museum. Visitors from every region of the globe come to visit very old places and archaeological sites and the untold stories of the city are explained in a variety of museums and other venues equipped with modern tools such as guided, interactive, and animated computer-aided histories of the surrounding history.
Timeless Stories of Ancient Glory
Horclosing History Through 21st-Century Imagery Technology
The new 3D scanners, virtual headsets, and digital image vaults are reconstructing ancient Rome. These technologies offer historians and even amateurs the ability to visualize a reconstruction of Roman culture and architecture, which is cherished in book form. Consequently, the stories of ancient Rome are digitally cherished, granting the enduring stories of ancient Rome access to memoirs of countless pairs of eyes. Furthermore, the charm of ancient Rome becomes a colorful part of our legacy.
Going Further into Understanding: Rome's Enduring Foundations
Ancient civilization, like all other things in life, contains rich lessons for their ancestors. As we step further into the 21st century, the evolution of ancient governance systems or culture, and the temples of wonderment have more to offer for many of the problems that modern day civilization face. In absorbing these, the upcoming generation can remember Ancient Rome for praising its modern spellbound architecture, instead of condoning its shattered “glory” whilst moving into the future.
Conclusion
The ancient Romans leave behind a legacy of splendor, advancement, and impact, first ever rich in civilization. The history of Rome has from the beginning, and will always be, a matter of relentless pride and development and prosperity of it. The city's constant presence is a reminder of the beauty of ancient history. There are dazzling aspects of Rome each and every person ought to hold dearly within their memory and wonder in awe as it represents a rich source of inspiration to the polish civilization.
Related Posts
Creating a Welcoming Worship Space: Tips for Choosing Inclusive Church Chairs
An inviting and inclusive church environment is paramount for fostering a strong sense of community and belonging. While theological beliefs and welcoming greetings are essential, the physical space itself also plays a significant role. One often-overlooked element that can significantly impact inclusivity is your church seating. This post dives...
Read MoreCaligula: Madness and Infamy in the Roman Empire
The name Caligula is synonymous with madness and infamy in the annals of Roman history. Gaius Julius Caesar Augustus Germanicus, known as Caligula, was the third Roman Emperor, and his tumultuous reign left an indelible mark of cruelty, debauchery, and tyranny. In this article, we delve into the life and...
Read MoreClaudius: The Unexpected Emperor and His Surprising Achievements
In the annals of Roman history, the name Claudius stands out as a remarkable story of an unexpected emperor who defied the odds and left behind a legacy of significant achievements. Often underestimated due to physical disabilities, Claudius rose to power and proved to be a capable and innovative ruler....
Read MoreFrom Ancient Rome To Today: 4 Games Played By Emperors And Their Modern Equivalents
In history, Ancient Rome had rulers who enjoyed games that involved intelligence and risk-taking. The interesting part is that some of these games have now evolved to their modern versions that still entertain people. When we look at the Ancient Roman history of emperors having fun, most of them went for...
Read MoreNero: The Notorious Emperor Who Fiddled While Rome Burned
The name Nero is synonymous with tyranny, extravagance, and the infamous image of an emperor who, according to legend, played the fiddle while Rome was engulfed in flames. Nero's reign is a dark chapter in the history of the Roman Empire, marked by cruelty, decadence, and the disastrous Great Fire...
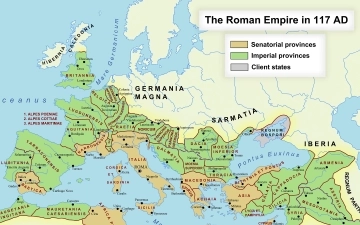
Read MoreThe Colossal Footprint: Exploring the Roman Empire at its Greatest Extent
The Roman Empire, a name that evokes images of gladiatorial combat, sprawling aqueducts, and stoic emperors, wasn't just a powerful state; it was a colossal empire that stretched across continents. But how vast was its reach at its zenith? This post delves into the greatest extent of the Roman Empire,...
Read More