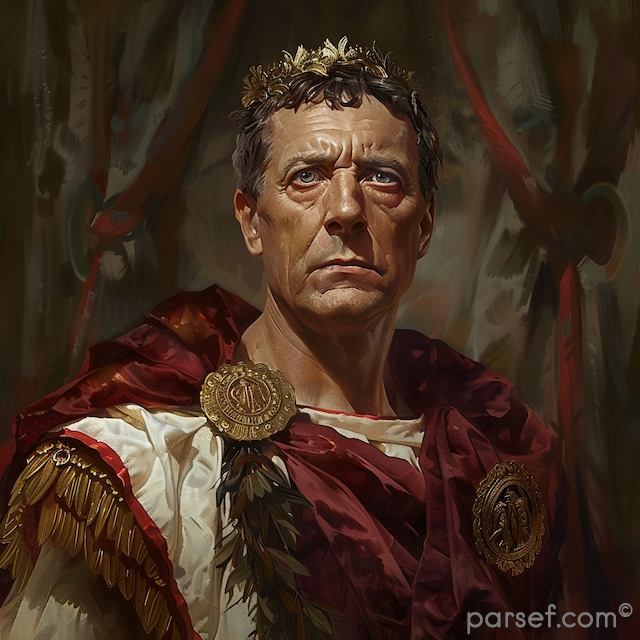
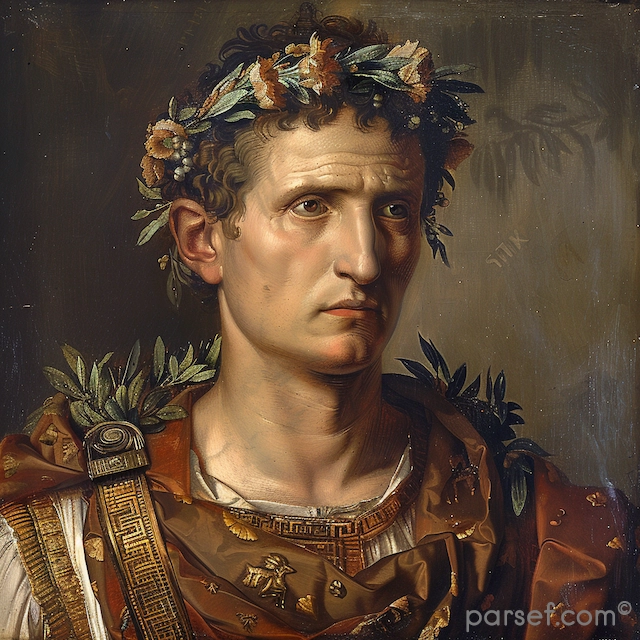
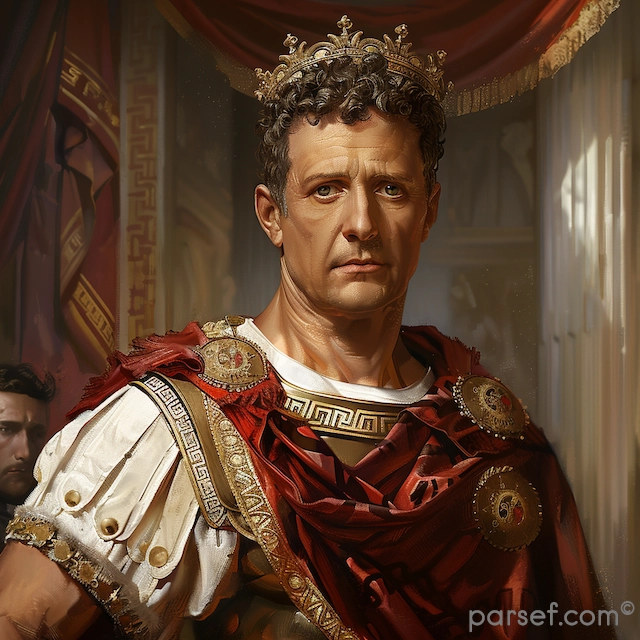
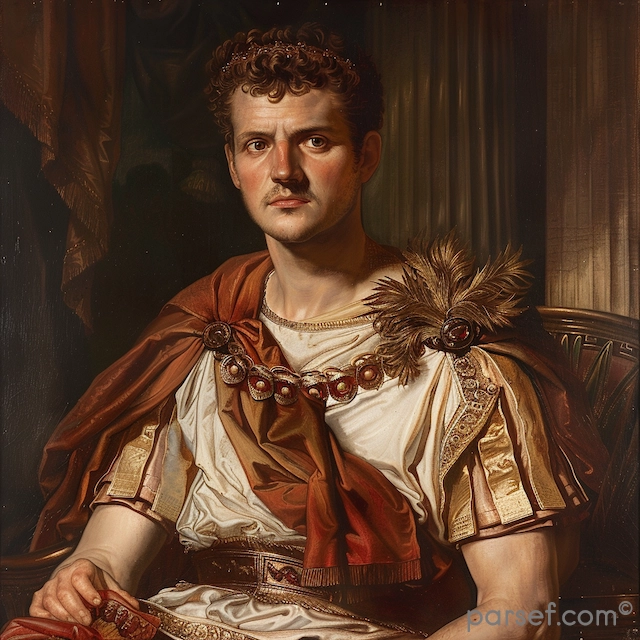
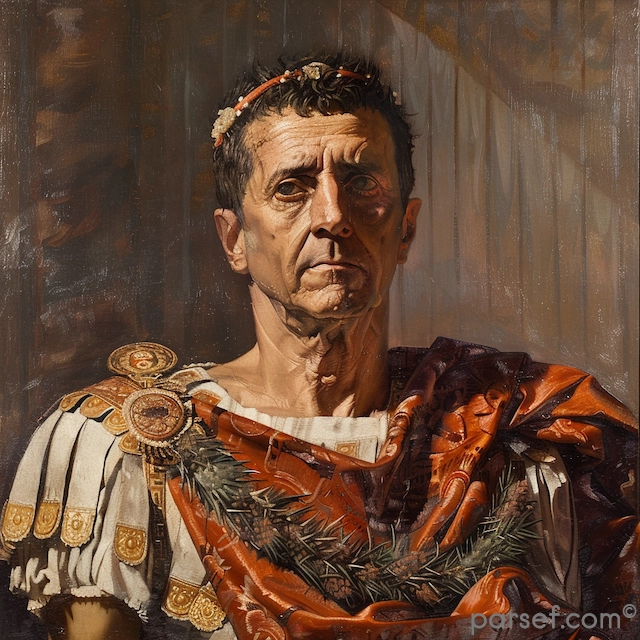
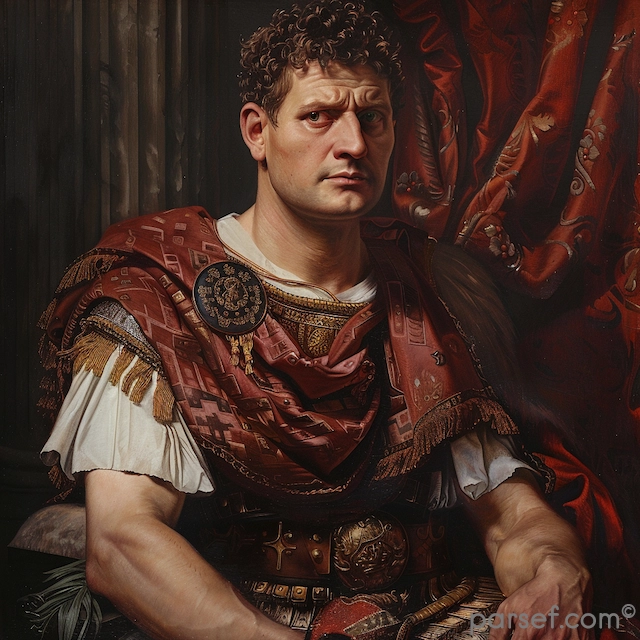
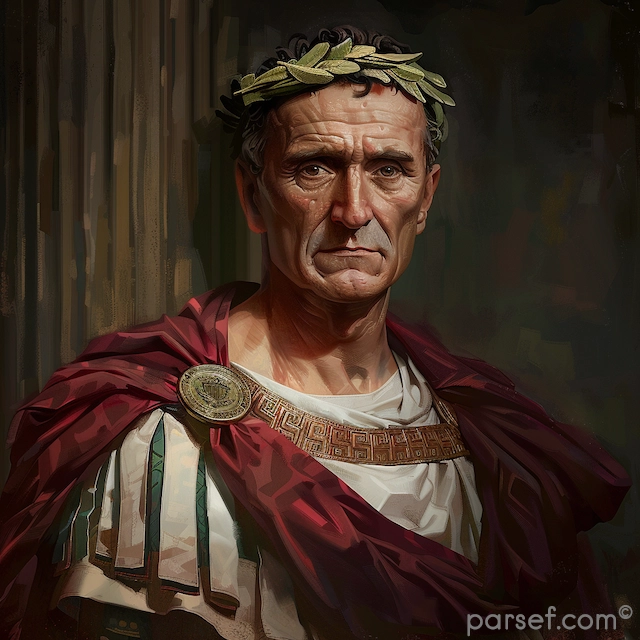
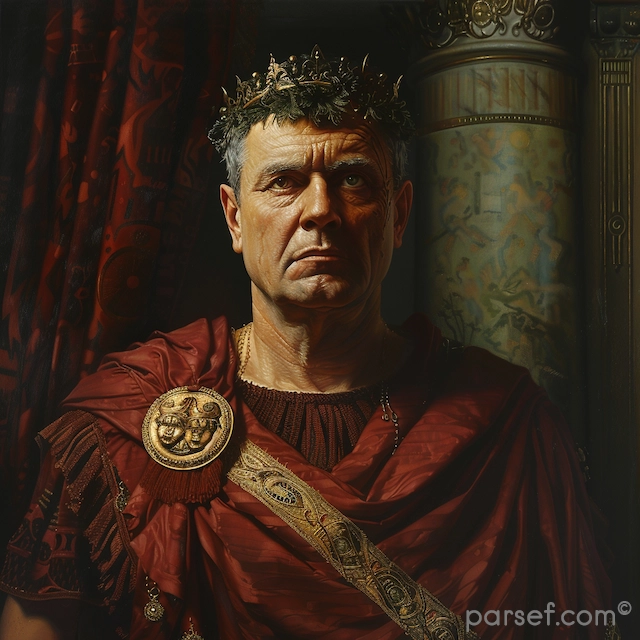
Trajan: Expanding the Roman Empire to Its Zenith
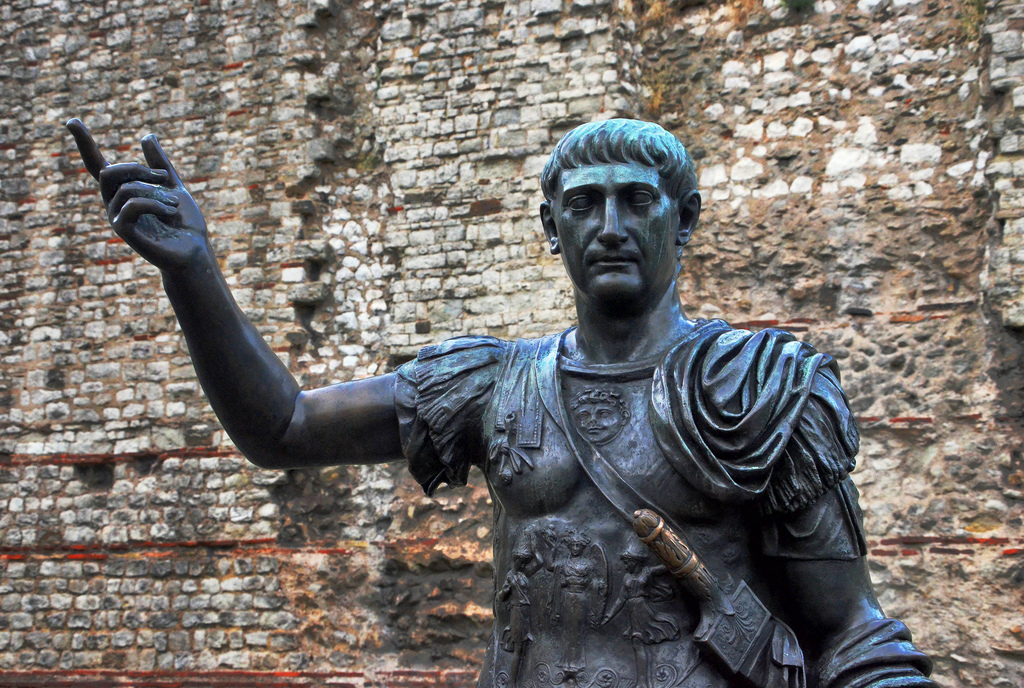

The Roman Empire, at its zenith, was a sprawling realm that stretched from Britannia in the north to Egypt in the south, and from Hispania in the west to Mesopotamia in the east. Among the emperors who played a pivotal role in this expansion and solidified Rome's dominance was Trajan. His reign, from 98 to 117 CE, marked a high point in Roman history, both in terms of territorial conquest and cultural achievement. In this article, we delve into the life and accomplishments of Trajan, the emperor who expanded the Roman Empire to its zenith.
Early Life and Rise to Power
Trajan, born Marcus Ulpius Trajanus in 53 CE, came from a distinguished provincial family in Spain. His family had a history of military service, and Trajan's own career followed suit. He rose through the ranks of the Roman military, earning a reputation for competence and leadership.
Adoption and Accession
Trajan's path to the imperial throne was unconventional. He was not born into the Julio-Claudian dynasty but was adopted by Emperor Nerva, who saw in Trajan a capable and deserving successor. This adoption established a tradition of adopting capable successors, known as the "Adoptive Emperors."
Conquests and Expansion
Trajan's reign is most renowned for its extensive military campaigns. He launched several successful campaigns that significantly expanded the Roman Empire:
- Dacia (Modern-Day Romania): Trajan's conquest of Dacia, a prosperous region north of the Danube, brought vast wealth and resources to Rome.
- Parthia (Modern-Day Iran): His eastern campaigns led to the capture of the Parthian capital, Ctesiphon, and briefly brought Mesopotamia under Roman control.
- Armenia and Mesopotamia: Trajan's conquests in these regions further extended the Roman frontiers in the east.
These campaigns contributed to the territorial peak of the Roman Empire, which stretched from the Atlantic Ocean to the Persian Gulf.
Architectural and Cultural Achievements
Trajan was not only a skilled military strategist but also a patron of the arts and architecture. He commissioned several impressive public works, including Trajan's Column in Rome, which commemorates his Dacian campaigns and serves as a historical record of the era. He also undertook extensive public building projects, including roads, bridges, and aqueducts, enhancing the infrastructure of the empire.
Death and Legacy
Trajan's reign came to an end with his death in 117 CE. He was succeeded by his adopted son, Hadrian. Trajan's legacy endures as one of the "Five Good Emperors" of Rome, a period characterized by stability, prosperity, and competent governance.
Trajan's military conquests and cultural contributions left an indelible mark on Roman history. His reign is often regarded as the pinnacle of Roman expansion and power, and his legacy as a wise and capable ruler continues to be celebrated in both historical records and modern scholarship.
Trajan's reign represents a golden era of Roman history marked by territorial expansion, cultural achievements, and effective governance. His ability to combine military prowess with a commitment to civic and cultural development solidified his place among Rome's greatest emperors.
Related Posts
The Role of Horses in the Roman Empire: From War to Sport
If we look back on the Roman Empire, we can see that horses played an important role. They were engines of power and symbols of prestige, and they were used for agriculture, traveling, warfare, and yes, entertainment like chariot races. Spanning centuries of conquest and culture, horses have always been closely...
Read MoreFrom Scrolls to Stones: How Museums Document Biblical History
The Bible is more than just a collection of sacred texts—it’s a living document that has shaped centuries of religious, cultural, and historical movements. For thousands of years, it has been passed down through oral traditions, written manuscripts, and monumental inscriptions. The story of how these texts came to be,...
Read MoreRoman Emperors and the Importance of the Catholic Jubilee of 2025
Throughout history, Roman emperors have played a crucial role in shaping the world, particularly in their influence over politics, religion, and culture. Their legacy continues to resonate today, especially in the traditions of the Catholic Church. One such tradition is the Catholic Jubilee, a sacred year of forgiveness, renewal, and...
Read MoreUnearthing History: Julius Caesar’s Artifacts and Their Significance
Julius Caesar, one of the most renowned figures of Roman history, left an indelible mark on the ancient world. His military conquests, political reforms, and dramatic death have made him a central figure in historical and archaeological studies. Although Caesar lived over two millennia ago, numerous artifacts associated with his...
Read MoreSodom and Gomorrah: The Rise and Fall of Two Ancient Cities
Sodom and Gomorrah are two of the most infamous cities mentioned in ancient religious texts, notably the Bible. For centuries, they have symbolized divine judgment, moral depravity, and catastrophic destruction. Their story is told in the Book of Genesis, and echoes of their downfall reverberate through theology, archaeology, and mythology....
Read MoreThe Perfect French Riviera Wedding
The French Riviera: A Timeless Wedding Destination The French Riviera, or Côte d’Azur, is one of the world’s most iconic destinations for weddings, offering breathtaking coastlines, luxurious estates, and a romantic Mediterranean backdrop. But beyond its modern allure, this glamorous stretch of land has a deep-rooted history that dates back to...
Read More